Rate of reaction stating the number of chemical reactions that take place per unit time. The reaction rate stated molarity of the solute in the reaction generated each second reaction.
MAXWELL-BOLTZMANN DISTRIBUTION CURVE
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution describes the speed of the particles in the gas and the particles do not constantly interact with one another, but move freely between short collisions.
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution is usually regarded as the velocity distribution of molecules, but can also refer to the distribution of velocity, momentum, and the magnitude of the momentum of the molecule, which each will have a different distribution probability function, all of which related.
FACTOR AFFECTING THE RATE OF REACTION
The reaction rate is influenced by several factors, among others:The surface area
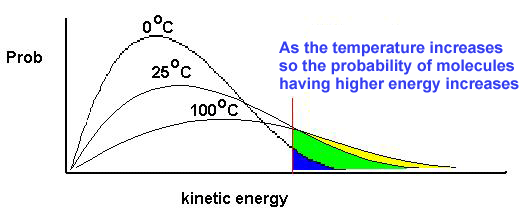
Temperature also plays a role in affecting the rate of reaction. When the temperature in a reaction that berlangusng raised, it causes particles to move more actively, so that collisions are more frequent, causing the reaction rate increases. Conversely, if the temperature is lowered, the increasingly active particles, so that the reaction rate is getting smaller.
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notion of heat and cold.
Catalyst

A catalyst is a substance that accelerates a chemical reaction rate at a certain temperature, without any changes or unused by the reaction itself. A catalyst role in the reaction but not as a reactant or a product. The catalyst allows the reaction to proceed faster or allow reaction at lower temperatures due to the changes it has triggered the reagent. Catalyst provides a path selection with lower activation energy. The catalyst reduces the energy required for reacting.MolarityMolarity is the number of moles of solute per unit volume of solvent. His relationship with the rate of reaction is that the bigger the molarity of a substance, the more quickly a reaction takes place. Thus in a low molarity reaction will be slower than a high molarity.ConcentrationBecause the rate equation is defined in the form of the reactant concentration with increasing concentration of the reaction speed of the ride anyway. This means that the higher the concentration, the more the reactant molecules are available, thus the possibility of colliding more and more as well so that the reaction rate increases. So the higher the concentration, the faster the rate of reaction
EQUATION
For the common reaction:
aA + bB → cC + dD
Example :
1. The reaction rate of a gas expressed as ν = x [A] [B]. Determine the ratio of the rate of reaction compared to the reaction rate early if:
a) the volume occupied by the gases reduced to half its original volume
b) the volume occupied by the gases reduced to 1/4 its original volume
Discussion:
a) the volume occupied by the gases reduced to half its original volume
That is, the concentration of the solution to 2 times the original. so :

b) the volume occupied by the gases reduced to 1/4 its original volume
That is, the concentration of the solution to 4 times the original. so :

2. Take a look on the reaction below :
2A + B ---> C + D
The following data about the reaction above were obtained from three experiments:
Calculate the rate expression in terms of [A] for experiment 1.
Exp. [A] [B] Initial rate of
formation of C1 0.6 0.15 6.3 x 10-3 2 0.2 0.6 2.8 x 10-3 3 0.2 0.15 7.0 x 10-4
Solution:
rate1 / rate3 = k1[A1]x[B1]y / k3[A3]x[B3]y k's will cancel and [B] will cancel
rate1 / rate3 = [A1]x / [A3]x
0.0063 / 0.0007 = (0.6)x / (0.2)x
9 = 0.6x / 0.2x
9 = 3x
rate = k[A]2
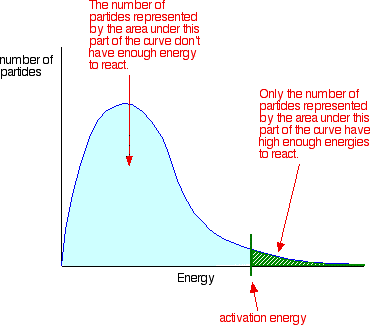
3. The curve below represents the distribution of molecular energies at a temperature T1 for a mixture of gases which react with each other. A is the activation energy for the reaction.

-
- Label the vertical axis.
- Explain the meaning of the term activation energy.
- Draw a second curve on the same axes and label it T2, for the same mixture at a lower temperature.
- By reference to the curves, state and explain in molecular terms the effect of reducing the temperature on the rate of reaction.
- The reaction is repeated in the presence of a catalyst.
- Mark on the energy axis a possible activation energy B for the catalysed reaction.
- State and explain in molecular terms the effect of the catalyst on the rate of reaction
Answer :

1.- Activation energy is the minimum energy required to break the bonds and start the reaction. - At a reduced temperature, the rate drops as fewer molecules possess the minimum energy, A, required to react.
2. With a catalyst, the rate increases as more molecules have the minimum energy, B, required to react.
No comments:
Post a Comment