Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that made no more than carbon and hydrogen. It is possible to bind two or three formed between carbon atoms, and even to the structure formed as a ring.
TYPES OF HYDROCARBON COMPOUNDS
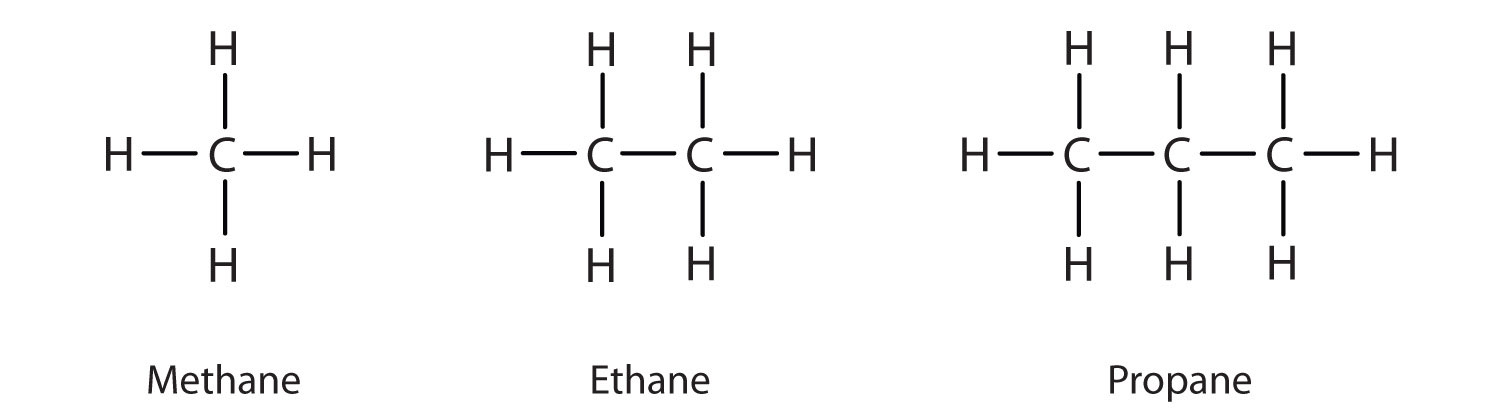
Alkanes
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons which means they are compounds with a single bond between atoms. Saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with hydrogen is the simplest. They are generally represented by the chemical formula CnH2n + 2 in the case of non-cyclic structure or straight-chain structure.
Alkane compound names:
Alkenes
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons which means they are compounds with one or more double bonds between carbon atoms. Special alkenes are those of unsaturated hydrocarbons that have at least one double bond. They are represented by the chemical formula CnH2n in general when there is no other functional groups. They are also called olefins. Alkenes have a pi bond between carbon atoms, and when subjected to a lot of reactions that break the pi bond in order to form a single bond so that they are more reactive than alkanes but relatively stable compared with the alkyne.
Alkenes naming:
From the table of Alkanes naming above, you just need to replace -ane with -ene. For the alkyl group still the same.
Alkyne
Alkyne also unsaturated hydrocarbons, they have one or more triple bonds between carbon atoms. Their general formula is CnH2n-2, in any case is a non-cyclic compound. They are also known as Acetylene. Alkynes are more reactive than alkenes and alkanes, they are many displays as polymerization and oligomerization. Polyethylene polymer formed called the show semiconductor properties. They are highly reactive due to the presence, unsaturated triple bond and subject to addition reactions.
Alkynes naming:
From the table of Alkanes naming above, you just need to replace -ane with -yne. For the alkyl group still the same.
REACTIONS IN HYDROCARBON
Combustion
All of hydrocarbon compounds if doing combustion reaction will produce Carbon Dioxyde (CO2) and Water (H2O).
example :

Reaction in alkanes
Free Radical Substitutionreactions in which one atom in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms. Free radical substitution often involves breaking a carbon-hydrogen bond in alkanes.

Reaction in Alkenes and Alkynes
Addition
The addition means adding or arrest. In addition reaction, a substance added to the compound C which has a double bond, so the bond was changed to a single bond. On alkenes and alkynes, the reaction that occurs is electrophilic addition reactions.
references :
- http://www.masterorganicchemistry.com/2013/04/25/summary-alkene-reaction-pathways/
- http://www.masterorganicchemistry.com/2013/12/19/synthesis-reactions-of-alkanes/
- http://ilmualam.net/perbedaan-antara-alkana-alkena-alkuna.html
- http://www.kentchemistry.com/images/links/organic/add.png


No comments:
Post a Comment