DEFINITION
The chemical bonding is a bond that forms between atoms or between molecules by means of:
One atom loses electrons, while the other atoms accept electron
The use of shared pair of electrons originating from each atom bonded
The use of shared pair of electrons originating from one atom bonded
The purpose of chemical bond formation is to achieve the stability of an element. The stability of the element occurs when an element follow the octet rule. Octet rule is the tendency of these elements to make the electron same configuration as the noble gases. The noble gases (VIII-A group) have as many as eight valence electrons (octet) or 2 (duplet, only the element Helium).
CHEMICAL BONDING TYPES
1. Ionic Bond
Ionic bonds, is the bond formed by the transfer (handover) of electrons from one element to another element. Both these bonds binds to the electrostatic force. Elements that tend to release electrons adala metal element while the element that tends to accept electrons are non-metals.
"The bond that is formed when the metal element remove an electron and
is followed by non-metallic element that accepts electrons"In other words, the giving and the receivingExamples of ionic bonds are:Cl Na element with which to form the compound NaCl.11Na: 2,8,1 à Na +17Cl: 2,8,7 à ClNa + + Cl à NaClNa
element 1 valence electrons release so that the same electron
configuration with noble gas (8), and the element Cl accept one electron
in their outer shell so that the same electron configuration with noble
gas (8). If the element loses electrons, it is positively charged elements, but
if the elements accept electrons, the negatively charged elements.Compounds that have an ionic bond, among others:
Group alkali (IA) [except the H atom] with a halogen group (VIIa). Example: NaF, KI, and CsF
Group alkali (IA) [except the H atom] with oxygen group (VIA). Example: Na2S, Rb2S, Na2O
Alkaline earth group (IIA) with the oxygen group (VIA). Examples of "CaO, BaO, MGS.
2. Covalent BondsCovalent bond is a bond that occurs due to the use of pairs of electrons are shared by two atoms belikatan. A
covalent bond is due to the inability of one atom will bond to release
electrons, which in its formation, each atom has orbital in the outer
shell that contains a single electron. And the second orbial overlap (overlap) so that an electron pairs are formed, then used jointly by both atoms. Covalent bonds are formed by fellow non-metallic elements.
"Bond formed by the use of elektrom together between non-metallic elements"In other words, both giving and receivingExamples of covalent bonds:Elements H with N form a compound NH31H: 1 à H +7N: 2, 5 à N-3H + + N-3 à NH3Elements
H need one electron to satisfy the octet rule, while the N elements
requires three electrons to satisfy the octet rule. Therefore, these two elements together to give and receive (mutually wearing)Type - the type of covalent bond:
a. Based on the number of pairs of electrons, covalent bonds are divided into:
Single covalent bonds, is a covalent bond that uses one pair of electrons. Example: H-Cl, H-H
Double covalent bond, is a covalent bond that uses two pairs of electrons. Example: O = O
Triple covalent bonds, is a covalent bond that uses three pairs of electrons. Example: HCCH
b. Based on the polarity, the covalent bond is divided into:
Polar covalent bond, between two atoms with electronegativity berdeda (different elements). Example: H-Cl bond, H-F, N-H
Nonpolar covalent bond, between two atoms with equal electronegativity (the same element). Example: bond H-H, O = O, Cl-Cl
3. Dative Covalent Bonds
Dative Covalent bonding is the bond that is formed by the use
of shared pair of electrons originating from one atom bonded [Couples
Free Electron (PEB)], whereas the other atom can only accept pairs of
electrons are shared.
"The bond that is formed when the pair of electrons shared only comes from one of the elements that bind"In other words, no one receiving, and some do not accept
Examples of covalent coordination:
4. Metallic Bonds
Metal bond is a bond formed by the pull that occurs between the positive charge of metal ions to the negative charge of the electrons are free to move. Metal atoms can be likened to the ping-pong balls were crammed tightly together. Metal atom has few valence electrons, so it is easy to be released and form a positive ion. So that the electrons can move from one atom to another. The mobility of electrons in the metal-free manner, so that the valence electron delocalization metal experience that is a state where the valence electrons are not fixed position on one atom, but it's constantly moving from one atom to another. Valence electrons in the blend to form the electron cloud that surrounds the positive ions of metal.
5. Sigma and Pi Bonds
A double bond is one sigma and one pi bond. A triple bond is one sigma and two pi bonds. Pi bonds are always made from two P-orbitals. * Hydrogens do not have hybridized orbitals and will make sigma bonds with their S-orbital.
Sigma bond:
A covalent bond resulting from the formation of a
molecular orbital by the end-to-end overlap of atomic orbitals, denoted by the
symbol σ.
Now have a look at this illustration to see how this end-to-end overlapping occures:
Pi bond: A covalent bond resulting from the formation of a
molecular orbital by side-to-side overlap of atomic orbitals along a plane perpendicular to a line connecting the nuclei of
the atoms, denoted by the symbol π.
Here's another illustration showing how the side-to-side overlapping occurs:
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
Van Der Walls Force
Van der Waals forces can be divided into two types, namely style disperse and dipole-dipole force. Molecules can attract one another at a distance being and repel each other at close range. Attractive style are collectively called "van der Waals".
 Temporary dipoles (London forces)
Temporary dipoles (London forces)London forces are intermolecular interactions that occur nonpolar, nonpolar intermolecular either similar or different types of intermolecular nonpolar. London style is the style of the weakest. Nonetheless, their style of London causing nonpolar compounds can be melted or solidified.
Dipole - Dipole Forces

Dipole stands in polar, which means that two poles. Compounds that have the dipole is a compound that has a positive pole (δ +) on the one hand, and the negative pole (δ-) on the other side. Compounds that have a dipole commonly referred to as polar compounds. Polar compounds via polar covalent bond is formed. It should be noted that in contrast to ion dipole. Owned electric dipole strength is weaker than the electric force ions.
In polar compounds, not separation. Molecule is a unity. Only on one side / edge there is a positive pole (δ +) and on the side / the other edge there is a negative pole (δ-).
Induced dipole forces
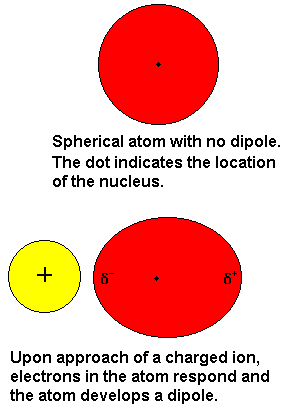 Such molecules style occur between polar molecules with nonpolar molecules. Dipoles of polar molecules will induce nonpolar molecules around it, so it had a dipole moment. The result is an electrostatic attraction force between dipole and dipole moment.
Such molecules style occur between polar molecules with nonpolar molecules. Dipoles of polar molecules will induce nonpolar molecules around it, so it had a dipole moment. The result is an electrostatic attraction force between dipole and dipole moment. Hydrogen Bonds
 Hydrogen bonds are the bonds between molecules that have the H atoms bonded to atoms which have a high keelektronegatifitas. Hydrogen
bonding can also be defined as a kind of intermolecular attractive
force between two partial electric charge with opposite polarity. Although stronger than most of the intermolecular forces, the hydrogen bond is much weaker than covalent and ionic bonds. Hydrogen bonds such as dipole-dipole interactions of Van der Waals. The difference is a partial positive charge comes from a hydrogen atom in a molecule. While
the partial negative charge derived from a molecule that is built by
atoms that have a large electronegativity, such as Flor atom (F), oxygen
(O), nitrogen (N). Partial negative charge comes from its lone pair.
Hydrogen bonds are the bonds between molecules that have the H atoms bonded to atoms which have a high keelektronegatifitas. Hydrogen
bonding can also be defined as a kind of intermolecular attractive
force between two partial electric charge with opposite polarity. Although stronger than most of the intermolecular forces, the hydrogen bond is much weaker than covalent and ionic bonds. Hydrogen bonds such as dipole-dipole interactions of Van der Waals. The difference is a partial positive charge comes from a hydrogen atom in a molecule. While
the partial negative charge derived from a molecule that is built by
atoms that have a large electronegativity, such as Flor atom (F), oxygen
(O), nitrogen (N). Partial negative charge comes from its lone pair.Factors that influence the style of the attraction between molecules (H atoms and other atoms):- Electronegativity, is a measure of the tendency of atoms to attract bonding electron pairs. If the atoms are equally electronegative, both have the same tendency to attract the bonding pair, and therefore will find half the average between two atoms, for example, the molecules H2 or Cl2. "The greater the difference in electronegativity of atoms in a molecule or intermolecular, the stronger the hydrogen bond"- Polarity, is the polarity of a substance that binds with other elements and there are a couple of free electrons at the molecular center .. "The more pairs of free electrons (electron pair not bonded), the more readily form hydrogen bonds".
Effect of Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces affect the physical properties of a substance or compound. Some physical properties that include boiling point and surface tension.
1. Boiling pointThe boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the vapor pressure equal to the pressure of fluid leaving the outside. If it happens, it will form in the liquid vapor gelembunggelembung. Because the vapor pressure inside the bubble is equal to the vapor pressure of the air, so bubbles can push themselves through the surface and move into the gas phase above the liquid. Such a state is called boiling. The boiling point of a substance also describes the energy required to overcome the intermolecular attractive forces in the substance. If the attractive force is getting stronger
2. The surface tension (surface tension)The surface tension (surface tension) is a style that tends to create a curved liquid surface. This is because on the surface of the liquid is less than the number of molecules of molecular liquid water beneath the surface. As a result, the molecules at the surface experiences a force of attraction is so weak that the molecules tend to gravitate to the surface. Either in droplets or liquids in contact with the place, then it has a curved surface area as small as possible in such an atmosphere to minimize surface energy.

No comments:
Post a Comment